Polypectomy in dogs and cats
Polypectomy represents the surgical removal of polyps. In our clinic we remove polyps using minimally invasive method – endoscopic. During endoscopic procedures, such as colonoscopy, polyps can be removed by forceps that are introduced through the endoscope. Larger polyps may be removed using the loop around the base of the polyp, after which the cauterizing is executed in order to prevent bleeding.
The polyp is an abnormal mass of tissue that grows into and out of the mucous membranes inside the animal’s organism. The polyps have the potential to be malignant, and therefore in the event of their occurrence should be removed.
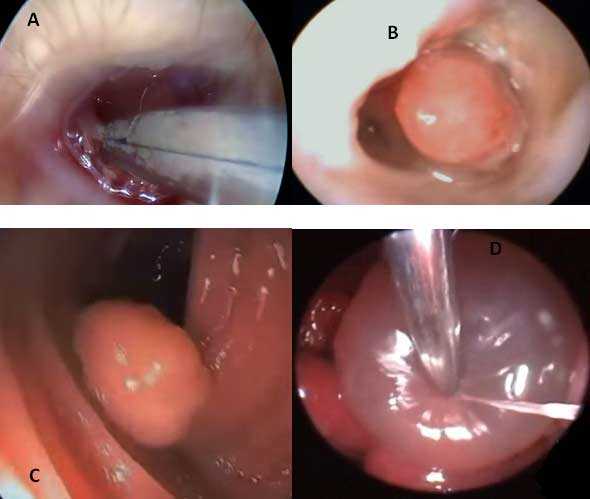
Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, uterus, bladder and nasal cavity, but can also be found in the ear canals as well as on any other surface of mucosal mucous membranes (Figure 1). The most common occurrence of polyps is not accompanied by specific symptoms, so they can remain undetected until specific diagnostic review of the patient, such as colonoscopy, rhinoscopy, gastroscopy etc. Once you identify the body recommended their removal. Even if the biopsy is satisfied that the non-cancerous they always have the potential to become, if not removed.
Endoscopic polypectomy as a procedure in the clinic IVAVET carried out by professionals who have undergone specialized training and have extensive experience in this field.
After removing polyps from the body, they are sent for further histopathological examination, to determine whether there is in them cancerous or precancerous cells. After the result obtained the owner of the patient will be informed, and if it turns out to be malignant polyp will be invited for further testing.
Bearing in mind that, generally, polyps are asymptomatic, owners must keep in mind that it is sometimes necessary to perform a general health check on their pet for early diagnosis of any pathological changes.
Nasal polyps in dogs
Nasal polyps (Figure 1) relating to the protruding pink polypoid growths are usually benign, which grow out of the nasal mucous membranes – the moist tissue that lines the nose. Symptoms that occur as a result of the development of polyps in the nose remind and mimic diseases such as colds, but can not be withdrawn solely giving antibiotics.
The symptoms of the onset of nasal polyps in dogs
Depending on the location of polyps symptoms may vary
- Nasalna cavity:
- Mucous discharge
- The formation of scabs in the nose
- Nosebleed
- Obstruction of nasal patency ways
- Maxillary sinus:
- Hematoma of the face or below eye
-
Frontal sinus:
- Hematoma on the forehead
- Ethmoid sinus:
- Obstruction of nasal patency ways
The most common types of benign polyps in the oral cavity of dogs:
- Nasal polyps
- Reverse polyps – Polyps like nipples
- Hemangiomas
- Osteomas – tumors of the bone tissue of the nose
- Fibrous dysplasia – abnormal growth of bone tissue in the nose
- Angiofibroma – growths consisting of fibrous tissue and blood vessels
The causes of nasal polyps in dogs
There is no clearly defined cause that leads to benign nasal polyps in the nasal pathways. As a possible etiological causes viral, bacterial infections and chronic inflammation and swelling of mucous membranes in the nose are cited.
Diagnosis of nasal polyps in dogs
In order to establish the diagnosis of polyps in dogs they need to be introduced in the anesthetic stage so the vet is able to make a detailed examination of the nasal cavity. Polyps are usually morphologically brilliant red, pink or gray growths in the area of the nasopharynx.
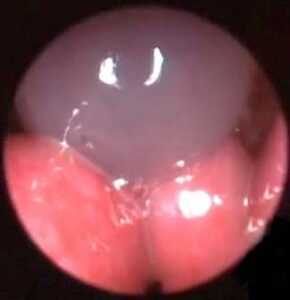
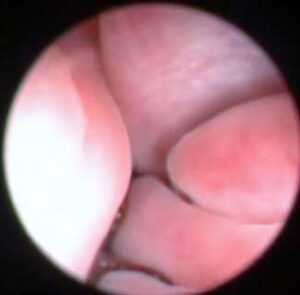
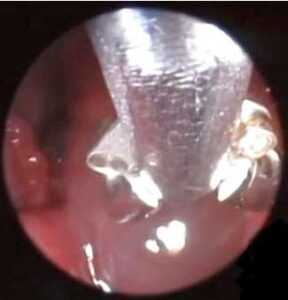
In order to make a diagnosis in the IVA VET clinic we use rhinoscopy (Figure 2) and introduce into the nasal cavity a flexible endoscope (a thin cable with a specialized camera, Figure 3). Also, it is necessary to perform a biopsy specimen (Figure 4) to determine the nature of the growths. After histopathological results obtained veterinarian still determining treatment approach in order to cure.
The treatment of nasal polyps
Main, safest and most effective treatment of nasal polyps is their surgical removal (Figure 5)
This surgery is a simple and routine procedure.
In our clinic this intervention is performed using appropriate endoscopic instruments.
It is very important to completely remove the root, the base and the handle of polyps in order to prevent relapses. After surgery you will be prescribed the appropriate medications, in order to prevent the occurrence of secondary fungal or bacterial infections.
Bearing in mind that there is still not clearly defined etiologic causal nasal polyps, there is no preventive measures that could be recommended.